Introduction to Deep Learning and Self-Driving Cars
1. 강의 개요
1.1 주요 학습 주제
- Deep Reinforcement Learning
- Convolutional Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
위 기술들을 이용하여 autonomous driving완성
- perception, localization, mapping, control, planning, driver state
1.2 목표
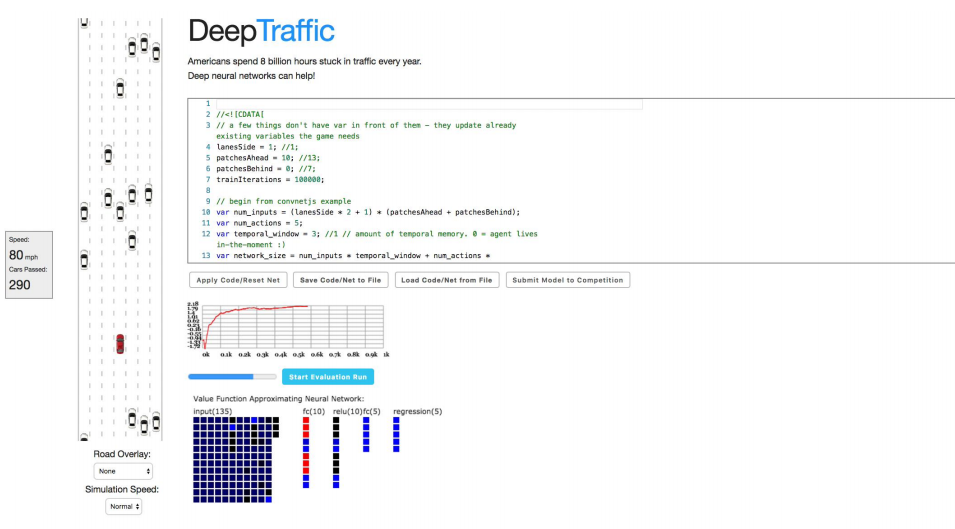
A. Project DeepTraffic
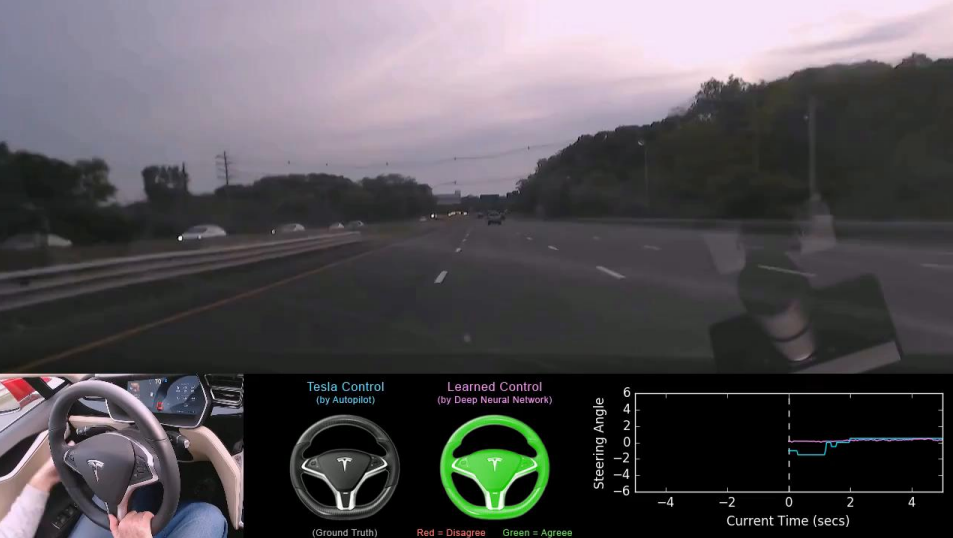
B. Project DeepTesla
2. 자동 주행시 필요한/해결해야하는 기술/정보들
- Localization and Mapping: Where am I?
- Scene Understanding: Where is everyone else?
- Movement Planning: How do I get from A to B?
- Driver State: What’s the driver up to?
History
- DARPA Grand Challenge II (2006) : Stanford’s Stanley wins
- DARPA Urban Challenge (2007) : CMU’s Boss (Tartan Racing) wins
3. 뉴런
- Human brain: ~100-1,000 trillion synapses
- (Artificial) neural network: ~1-10 billion synapses
3.1 Perceptron Algorithm
Provide training set of (input, output) pairs and run:
- Initialize perceptron with random weights
- For the inputs of an example in the training set, compute the Perceptron’s output
- If the output of the Perceptron does not match the output that is known to be
correct for the example:
- If the output should have been 0 but was 1, decrease the weights that had an input of 1.
- If the output should have been 1 but was 0, increase the weights that had an input of 1.
- Go to the next example in the training set and repeat steps 2-4 until the Perceptron makes no more mistakes
뉴런의 기본 설명 : 입력 - weigh - Sum up - Activate - 출력
3.2 Neural Networks are Amazing
히든 레이어를 포함한 멀티 레이어 설명
- Special Purpose Intelligence : Supervised learning??
- General Purpose Intelligence : Unsupervised learning or Reinforcement Learning ??
핑퐁 게임을 예시로 설명
3.3 Current Drawback
- Lacks Reasoning:
- Humans only need simple instructions: “You’re in control of a paddle and you can move it up and down, and your task is to bounce the ball past the other player controlled by AI.”
- Requires big data: inefficient at learning from data
- Requires supervised data: costly to annotate real-world data
- Need to manually select network structure
- Needs hyperparameter tuning for training:
- Learning rate
- Loss function
- Mini-batch size
- Number of training iterations
- Momentum: gradient update smoothing
- Optimizer selection
- Defining a good reward function is difficult…
3.4 What changed?
- Compute : CPUs, GPUs, ASICs
- Organized large(-ish) datasets : Imagenet
- Algorithms and research: Backprop, CNN, LSTM
- Software and Infrastructure : Git, ROS, PR2, AWS, Amazon Mechanical Turk, TensorFlow, …
- Financial backing of large companies : Google, Facebook, Amazon, …

3.5 Useful Deep Learning Terms

3.6 Traditional Machine Learning

- Edge, Corners, Contours등을 사용하는 방식. (이전 방식인가?)
- 각 항목을 사람이 이전에 정의 해주어야 함 (Hand Designed Feature)
3.7 Deep Learning Applications
색 칠하기, 고양이 구분, 번역등 여러 활용예 설명
할수 있는것도 있지만 못하는 것도 있음. Moravec’s Paradox: The “Easy” Problems are Hard
걷기, 중심 잡기등이 체스보다 더 어려움.
데이터 부족???
“Encoded in the large, highly evolved sensory and motor portions of the human brain is a
billion years of experience about the nature of the world and how to survive in it.…
Abstract thought, though, is a new trick, perhaps less than 100 thousand years old. We have
not yet mastered it. It is not all that intrinsically difficult; it just seems so when we do it.”
- Hans Moravec, Mind Children (1988)
- Visual perception: 540 millions years of data
- Bipedal movement: 230+ million years of data
- Abstract thought: 100 thousand years of data
그럼 자율 주행 자동차는 어려운가?
- Human performance(사고 확률): 1 fatality per 100,000,000 miles
- Error rate for AI to improve on: 0.000001%
Challenges:
- Snow
- Heavy rain
- Big open parking lots
- Parking garages
- Any pedestrian behaving irresponsibly or just unpredictably
- Reflections, dynamics blinding ones
- Merging into a high-speed stream of oncoming traffic
딥러닝은 완전하지 않다. 속이기 쉽다[1]. = 사고날 확률이 높다.
[1]: Nguyen et al. "Deep neural networks are easily fooled: High confidence predictions for unrecognizable images." 2015
3.8 What’s Next for Deep Learning? (5 year vision)
- Ilya Sutskever, Research Director of OpenAI: Deeper models, models that need fewer examples for training.
- Christian Szegedy, Senior Research Scientist at Google: Become so efficient that they will be able to run on cheap mobile devices.
- Pieter Abbeel, Associate Professor in Computer Science at UC Berkeley: Significant advances in deep unsupervised learning and deep reinforcement learning.
- Ian Goodfellow, Senior Research Scientist at Google: Neural networks that can summarize what happens in a video clip, and will be able to generate short videos. Neural networks that model the behavior of genes, drugs, and proteins and then used to design new medicines.
- Koray Kavukcuoglu & Alex Graves, Research Scientists at Google DeepMind: An increase in multimodal learning, and a stronger focus on learning that persists beyond individual datasets.
- Charlie Tang, Machine Learning group, University of Toronto: Deep learning algorithms ported to commercial products, much like how the face detector was incorporated into consumer cameras in the past 10 years.
3.9 딥러닝 라이브러리들
| 라이브러리 | 개발사 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensorflow | Automatic Differentiation | |
| keras | On top of Tensorflow | |
| Torch | closer to the details | |
| mxNet | Amazon | Interface: Python, R, Julia |
| Theano | 모트리올대학교 | One of the earlier frameworks |
| cuDNN | NVIDIA | CUDA onthe GPU |
| neon | Intel | Nervana was working on a neural network chip |
| caffe | Berkeley대 | Initial focus on computer vision |
| CNTK | MS | Mostly used at MS Research |