Euclidean Cluster Extraction
가장 간단한 방법으로 두 점사이의 거리 정보를 이용한다. Euclidean segmentation is the simplest of all. It checks the distance between two points.
- 거리가 특정 값보다 작다면 같은 클러스터로 간주 한다.
If it is less than a threshold, both are considered to belong in the same cluster.
It works like a flood fill algorithm:
- a point in the cloud is "marked" as "chosen" for the cluster.
- Then, it spreads like a virus to all other points that are near enough, and from those to even more points, until none new can be added.
- Then, a new cluster is initialized, and the procedure starts again with the remaining unmarked points.
import numpy as np
import pcl
cloud = pcl.load('./examples/pcldata/tutorials/table_scene_lms400.pcd')
# // Create the filtering object: downsample the dataset using a leaf size of 1cm
vg = cloud.make_voxel_grid_filter()
vg.set_leaf_size (0.01, 0.01, 0.01)
cloud_filtered = vg.filter ()
# // Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
seg = cloud.make_segmenter()
seg.set_optimize_coefficients (True)
seg.set_model_type (pcl.SACMODEL_PLANE)
seg.set_method_type (pcl.SAC_RANSAC)
seg.set_MaxIterations (100)
seg.set_distance_threshold (0.02)
i = 0
nr_points = cloud_filtered.size
# Creating the KdTree object for the search method of the extraction
tree = cloud_filtered.make_kdtree()
ec = cloud_filtered.make_EuclideanClusterExtraction()
ec.set_ClusterTolerance (0.02)
ec.set_MinClusterSize (100)
ec.set_MaxClusterSize (25000)
ec.set_SearchMethod (tree)
cluster_indices = ec.Extract()
print('cluster_indices : ' + str(cluster_indices.count) + " count.")
cloud_cluster = pcl.PointCloud()
for j, indices in enumerate(cluster_indices):
# cloudsize = indices
print('indices = ' + str(len(indices)))
# cloudsize = len(indices)
points = np.zeros((len(indices), 3), dtype=np.float32)
# points = np.zeros((cloudsize, 3), dtype=np.float32)
# for indice in range(len(indices)):
for i, indice in enumerate(indices):
# print('dataNum = ' + str(i) + ', data point[x y z]: ' + str(cloud_filtered[indice][0]) + ' ' + str(cloud_filtered[indice][1]) + ' ' + str(cloud_filtered[indice][2]))
# print('PointCloud representing the Cluster: ' + str(cloud_cluster.size) + " data points.")
points[i][0] = cloud_filtered[indice][0]
points[i][1] = cloud_filtered[indice][1]
points[i][2] = cloud_filtered[indice][2]
cloud_cluster.from_array(points)
ss = "cloud_cluster_" + str(j) + ".pcd";
pcl.save(cloud_cluster, ss)
Clustering
1. 유클리드 클러스터링
# Euclidean Clustering
def euclid_cluster(cloud):
white_cloud = XYZRGB_to_XYZ(cloud) # Apply function to convert XYZRGB to XYZ
tree = white_cloud.make_kdtree()
ec = white_cloud.make_EuclideanClusterExtraction()
ec.set_ClusterTolerance(0.015)
ec.set_MinClusterSize(20)
ec.set_MaxClusterSize(3000)
ec.set_SearchMethod(tree)
cluster_indices = ec.Extract()
return cluster_indices, white_cloud
def cluster_mask(cluster_indices, white_cloud):
# Create Cluster-Mask Point Cloud to visualize each cluster separately
#Assign a color corresponding to each segmented object in scene
cluster_color = get_color_list(len(cluster_indices))
color_cluster_point_list = []
for j, indices in enumerate(cluster_indices):
for i, indice in enumerate(indices):
color_cluster_point_list.append([
white_cloud[indice][0],
white_cloud[indice][1],
white_cloud[indice][2],
rgb_to_float( cluster_color[j] )
])
#Create new cloud containing all clusters, each with unique color
cluster_cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGB()
cluster_cloud.from_list(color_cluster_point_list)
return cluster_cloud
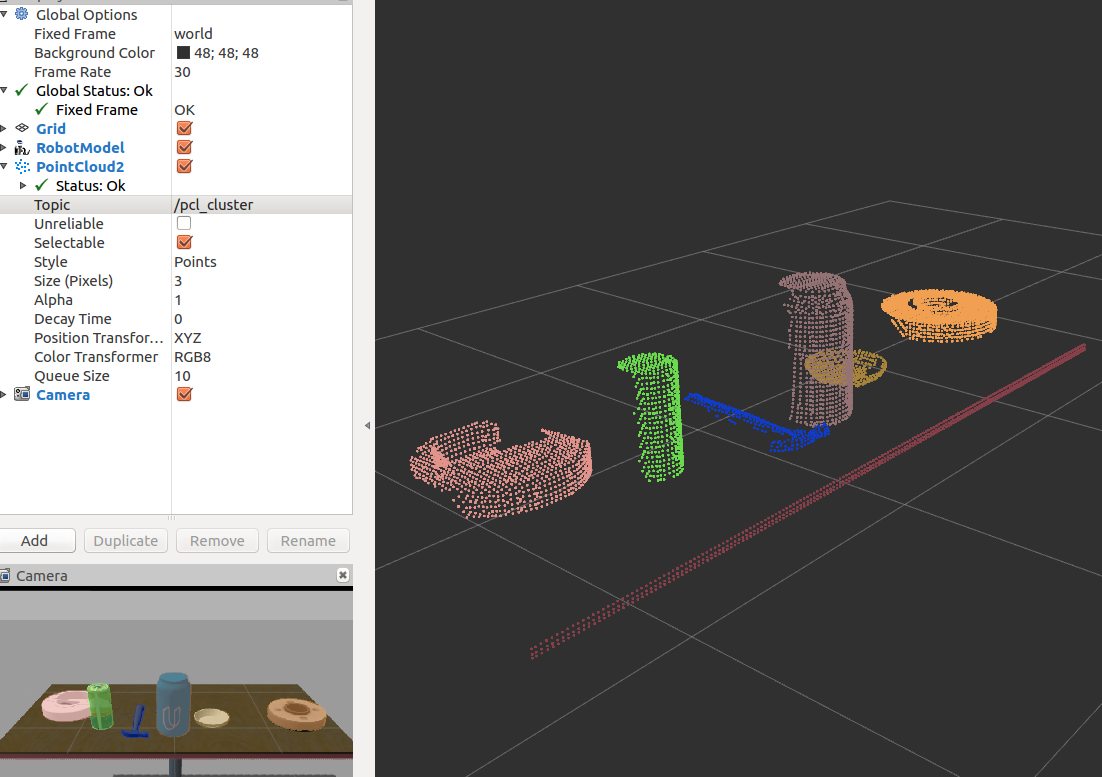
https://github.com/mithi/point-cloud-clusters
#!/usr/bin/env python
import numpy as np
import sklearn
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import pickle
from sensor_stick.srv import GetNormals
from sensor_stick.features import compute_color_histograms
from sensor_stick.features import compute_normal_histograms
from visualization_msgs.msg import Marker
from sensor_stick.marker_tools import *
from sensor_stick.msg import DetectedObjectsArray
from sensor_stick.msg import DetectedObject
from sensor_stick.pcl_helper import *
from pcl_helper import *
from filtering_helper import *
# This pipeline separates the objects in the table from the given scene
def split_cloud(cloud):
# Downsample the cloud as high resolution which comes with a computation cost
downsampled_cloud = do_voxel_grid_filter(point_cloud = cloud, LEAF_SIZE = 0.01)
# Get only information in our region of interest as we don't care about the other parts
filtered_cloud = do_passthrough_filter(point_cloud = downsampled_cloud,
name_axis = 'z', min_axis = 0.6, max_axis = 1.1)
# Separate the table from everything else
table_cloud, objects_cloud = do_ransac_plane_segmentation(filtered_cloud, max_distance = 0.01)
return objects_cloud, table_cloud
# This pipeline returns groups of indices for each cluster of points
# Each cluster of indices is grouped as belonging to the same object
# This uses DBSCAN Algorithm Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with noise
# Aka Eucledian clustering to group points
def get_clusters(cloud, tolerance, min_size, max_size):
tree = cloud.make_kdtree()
extraction_object = cloud.make_EuclideanClusterExtraction()
extraction_object.set_ClusterTolerance(tolerance)
extraction_object.set_MinClusterSize(min_size)
extraction_object.set_MaxClusterSize(max_size)
extraction_object.set_SearchMethod(tree)
# Get clusters of indices for each cluster of points, each clusterbelongs to the same object
# 'clusters' is effectively a list of lists, with each list containing indices of the cloud
clusters = extraction_object.Extract()
return clusters
# clusters is a list of lists each list containing indices of the cloud
# cloud is an array with each cell having three numbers corresponding to x, y, z position
# Returns list of [x, y, z, color]
def get_colored_clusters(clusters, cloud):
# Get a random unique colors for each object
number_of_clusters = len(clusters)
colors = get_color_list(number_of_clusters)
colored_points = []
# Assign a color for each point
# Points with the same color belong to the same cluster
for cluster_id, cluster in enumerate(clusters):
for c, i in enumerate(cluster):
x, y, z = cloud[i][0], cloud[i][1], cloud[i][2]
color = rgb_to_float(colors[cluster_id])
colored_points.append([x, y, z, color])
return colored_points
def get_normals(cloud):
get_normals_prox = rospy.ServiceProxy('/feature_extractor/get_normals', GetNormals)
return get_normals_prox(cloud).cluster
# Callback function for your Point Cloud Subscriber
def pcl_callback(pcl_msg):
# Convert ROS msg to PCL data
cloud = ros_to_pcl(pcl_msg)
# Extract objects and table from the scene
objects_cloud, table_cloud = split_cloud(cloud)
# Get a point cloud of only the position information without color information
colorless_cloud = XYZRGB_to_XYZ(objects_cloud)
# Get groups of indices for each cluster of points
# Each group of points belongs to the same object
# This is effectively a list of lists, with each list containing indices of the cloud
clusters = get_clusters(colorless_cloud, tolerance = 0.05, min_size = 100, max_size = 1500)
# Assign a unique color float for each point (x, y, z)
# Points with the same color belong to the same cluster
colored_points = get_colored_clusters(clusters, colorless_cloud)
# Create a cloud with each cluster of points having the same color
clusters_cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGB()
clusters_cloud.from_list(colored_points)
# CLASSIFY THE CLUSTERS
detected_objects_labels = []
detected_objects = []
for i, indices in enumerate(clusters):
cluster = objects_cloud.extract(indices)
# Convert point cloud cluster to ros message
cluster_msg = pcl_to_ros(cluster)
# Get features
color_hist = compute_color_histograms(cluster_msg, using_hsv = True)
normal_hist = compute_normal_histograms(get_normals(cluster_msg))
features = np.concatenate((color_hist, normal_hist))
# Predict and get label
prediction = classifier.predict(scaler.transform(features.reshape(1, -1)))
label = encoder.inverse_transform(prediction)[0]
detected_objects_labels.append(label)
# Get label position near object and publish in RViz
label_position = list(colorless_cloud[indices[0]])
label_position[2] += 0.4
object_markers_publisher.publish(make_label(label, label_position, i))
# Add detection to list of detected objects
detectedObject = DetectedObject()
detectedObject.label = label
detectedObject.cloud = pcl_to_ros(clusters_cloud)
detected_objects.append(detectedObject)
# Publish the list of detected objects
rospy.loginfo('Detected {} objects: {}'.format(len(detected_objects_labels), detected_objects_labels))
detected_objects_publisher.publish(detected_objects)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initialize ros node
rospy.init_node('object_markers_pub', anonymous = True)
# Create Subscribers
subscriber = rospy.Subscriber("/sensor_stick/point_cloud", pc2.PointCloud2, pcl_callback, queue_size = 1)
# Create Publishers
object_markers_publisher = rospy.Publisher("/object_markers", Marker, queue_size = 1)
detected_objects_publisher = rospy.Publisher("/detected_objects", DetectedObjectsArray, queue_size = 1)
# Load Model From disk
model = pickle.load(open('model.sav', 'rb'))
classifier = model['classifier']
encoder = LabelEncoder()
encoder.classes_ = model['classes']
scaler = model['scaler']
# Initialize color_list
get_color_list.color_list = []
# Spin
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
rospy.spin()